Endocrinology | Results of the Phase III GLORY 1 Clinical Trial in Chinese Adults with Obesity or Overweight Published in a Leading Medical Journal
纪立农团队针对中国超重或肥胖人群的Ⅲ期临床研究(GLORY-1)结果在权威期刊发表
2026-01-27
The team led by Professor Ji Linong of Peking University People’s Hospital published a research paper entitled “Once-Weekly Mazdutide in Chinese Adults with Obesity or Overweight” in The New England Journal of Medicine (IF = 78.5).

On May 24, 2025, results from the Phase III clinical trial GLORY 1, led by Professor Ji Linong of Peking University People’s Hospital and conducted in Chinese adults who are overweight or obese, were published in The New England Journal of Medicine. This study represents the first and only clinical trial worldwide of a GCG and GLP-1 dual receptor agonist for weight loss and glycaemic control that has been submitted for regulatory approval, and its publication in a leading international medical journal underscores its global significance.
For many years, global clinical guidelines for obesity management have been largely based on data from European and North American populations, with limited applicability to Asian populations. In response, Professor Ji’s team designed this clinical trial to address the distinct disease characteristics and treatment needs of Chinese individuals who are overweight or obese. The study demonstrated that all tested doses of mazdutide produced significant and sustained weight reduction compared with placebo, with nearly half of the participants achieving a weight loss exceeding 15 percent.
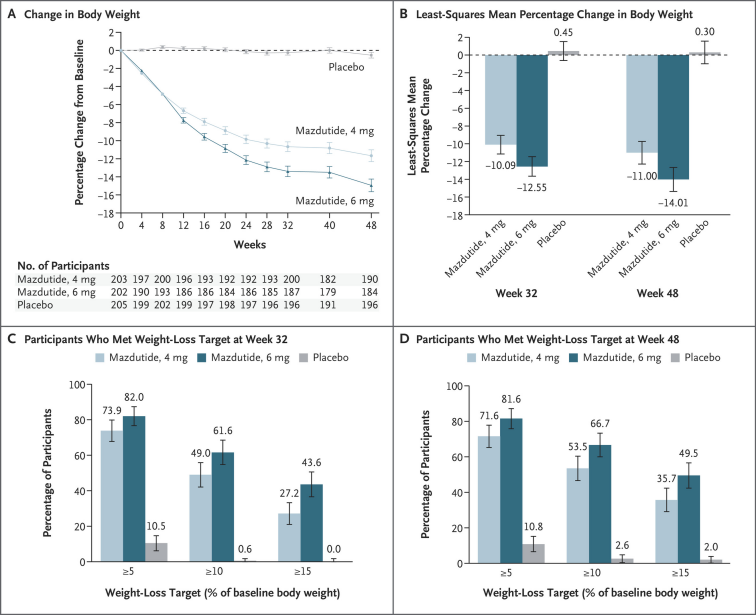
In addition to weight reduction, mazdutide showed broad metabolic benefits. The treatment was associated with significant improvements in key cardiometabolic indicators, including blood pressure, blood lipids, serum uric acid, and liver enzyme levels. Overall, the drug demonstrated a favorable safety and tolerability profile.
An accompanying editorial in The New England Journal of Medicine highlighted the comprehensive nature of the efficacy endpoints and discussed the future clinical potential of the therapy. Professor Ji Linong noted that the successful development of mazdutide is expected to accelerate the involvement of domestic pharmaceutical companies in obesity management and to support more personalized, full cycle care solutions for patients with overweight and obesity in China.

