Endocrinology and Metabolism | Prof. Ji Linong Shares New Research Findings at EASD 2024
纪立农教授牵头2型糖尿病全球创新药研究闪耀欧洲糖尿病年会
2024-10-18
The 60th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD 2024) was held from September 9-13, 2024, in Madrid, Spain. EASD is an academic non-profit organization. It aims to encourage and support research in the field of diabetes, facilitate the rapid diffusion of acquired knowledge and promote its application. As one of the largest diabetes conferences globally, its annual meeting attracts thousands of attendees, covering a wide range of topics from basic and clinical research to new diagnostic techniques and care practices.

On September 11, Professor Ji Linong from the Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism at Peking University People's Hospital (PKUPH) presented the findings of the COMBINE 1 study, marking the first time a Chinese researcher has served as the global leading principal investigator (PI) for a multi-regional clinical trial (MRCT) in diabetes.
The eagerly anticipated results of the COMBINE 1-3 studies were unveiled at the conference, capturing significant clinical attention. These Phase 3a trials evaluated the efficacy and safety of IcoSema across diverse groups of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) patients.
In an interview, Professor Ji Linong expressed his honor in leading this global research initiative alongside international colleagues. He also emphasized the growing trend of collaborative multi-center clinical studies in new drug development globally, which have been supported by the China Essentials program. This program aims to enhance China's participation in global clinical research, facilitating timely access to innovative treatments for Chinese patients.
Diabetes includes various types, such as type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes and others. According to China’s official data, rising adult obesity rates and an aging population have contributed to the increasing prevalence of diabetes, with T2DM accounting for over 90% of cases.
However, T2DM poses treatment challenges due to its complex nature, requiring long-term management and patient compliance. This has prompted researchers to search for more effective and convenient treatment methods. Currently, combination therapies featuring drugs with different mechanisms are a recommended strategy for managing T2DM. Among these therapies, the COMBINE 1 study is a multi-center, randomized and open-label Phase 3a clinical trial with researchers from multiple countries, promoting global collaboration in diabetes research.
The COMBINE series study assessed the efficacy and safety of IcoSema, the first once-weekly basal insulin/glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), in different T2DM patient populations. After over two years of research, the initial results were shared for the first time at the conference.
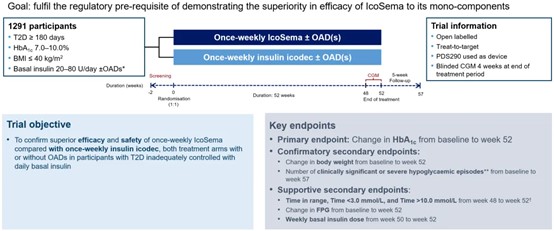
In the COMBINE 1 study, 1,291 adults with T2DM inadequately controlled on basal insulin were randomized to receive one of two treatments: IcoSema and insulin icodec alone for 52 weeks. Results indicated that IcoSema significantly improved blood glucose levels, reduced HbA1c, lowered hypoglycemia risk, and aided weight loss. As a once-weekly injection, IcoSema lessens the injection burden on patients, enhancing treatment satisfaction and compliance. In summary, IcoSema is expected to become a simpler, more effective and safer anti-diabetic medication, offering better outcomes for patients.
As the global Leading PI of the COMBINE 1 study, Professor Ji Linong played a pivotal role throughout the study's design, development and implementation of the protocol. In addition to the COMBINE series, Professor Ji Linong's team also presented other significant research findings at EASD 2024. These efforts not only advance the development and application of new anti-diabetic drugs but also enhance patient satisfaction and compliance, fostering international collaboration in diabetes research and offering new strategies for diabetes management. “The introduction of IcoSema is not only a significant innovation in drug development, but also an important attempt to ease the treatment burden and improve patient compliance based on patient-centered philosophy,” said Professor Ji Linong.
His team’s research achievements have contributed valuable experience to the global diabetes community, elevating China’s influence and standing in diabetes research worldwide.

