Urology | New Research Findings on Bladder Cancer Treatment by Prof. Xu Tao’s Team Published in Advanced Science
膀胱癌的CAR-T细胞免疫疗法:徐涛主任团队研究成果在权威杂志发表
2024-10-09
Recently, a research paper titled "Novel CAR-T Cells Specifically Targeting SIA-CIgG Demonstrate Effective Antitumor Efficacy in Bladder Cancer" was published online in the prestigious journal Advanced Science (IF=14.3) by the team led by Professor Xu Tao from the Department of Urology at Peking University People's Hospital (PKUPH), in collaboration with the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Science (CAS) and the School of Basic Medical Sciences at Peking University (PKU). The study reported a novel type of CAR-T cells that specifically target and eliminate bladder cancer cells expressing SIA-CIgG, demonstrating antitumor effects.

Dr. Ding Mengting, Dr. Lin Jiaxing, and Clinical Associate Professor Qin Caipeng from the same department at PKUPH served as the co-first authors of the paper. Professor Xu Tao, Researcher Wei Ping from SIAT of CAS and Professor Qiu Xiaoyan from the School of Basic Medical Sciences at PKU are the co-corresponding authors of the paper. PhD candidate Fu Yuhao from the Academy for Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies at PKU and Dr. Du Yiqing from the Department of Urology at PKUPH provided significant assistance for the study. This study received strong support from several official science foundation programs.
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy is a promising treatment method for bladder cancer (BC), the 10th most common malignant tumor in the world. However, its application in BC remains limited, partially because of the absence of appropriate target molecules. Therefore, it is of great significance to explore the application of CAR-T cell therapy in BC.
Sialylated cancer-derived IgG (SIA-CIgG) is highly expressed in most BC samples but displays limited expression in normal tissues. It is closely associated with malignant biological behavior in BC. However, its potential as a target for CAR-T cell therapy to treat BC is yet to be established. Researchers constructed the second-generation CAR-T cells using single-chain variable fragments (scFv) derived from its monoclonal antibodies. The results showed that CAR-T cells specifically targeting SIA-CIgG can effectively lyse BC cells and the cytotoxicity depends on SIA-CIgG expression. Furthermore, SIA-CIgG CAR-T cells demonstrate milder tumor cell lysis and enhanced persistence than human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) CAR-T cells, which have undergone extensive clinical trials. After repeated tumor antigen challenges, SIA-CIgG CAR-T cells display substantial alterations in both their transcriptome and chromatin accessibility. When combining SIA-CIgG CAR-T cell therapy with FDA-approved drugs to treat BC, the histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi), vorinostat, is found to enhance the ability of CAR-T cells for tumor cell lysis. This study suggests that the combination of SIA-CIgG CAR-T cells and vorinostat is promising for BC treatment.
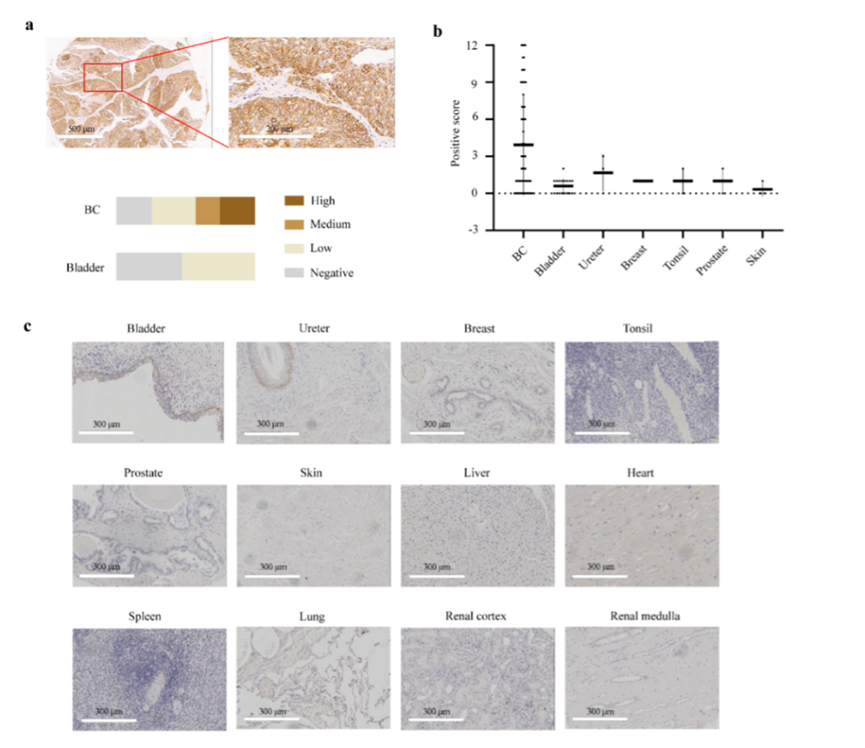
It is expected that CAR-T cell therapy can be applied in the BC treatment as soon as possible to provide a better treatment effect and improve the prognosis of the patient.
Paper Link: http://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39178136/

